|
Forecast Period
|
2026-2030
|
|
Market Size (2024)
|
USD 1.54 Billion
|
|
Market Size (2030)
|
USD 4.73 Billion
|
|
CAGR (2025-2030)
|
20.75%
|
|
Fastest Growing Segment
|
mHealth
|
|
Largest Market
|
North India
|
Market Overview
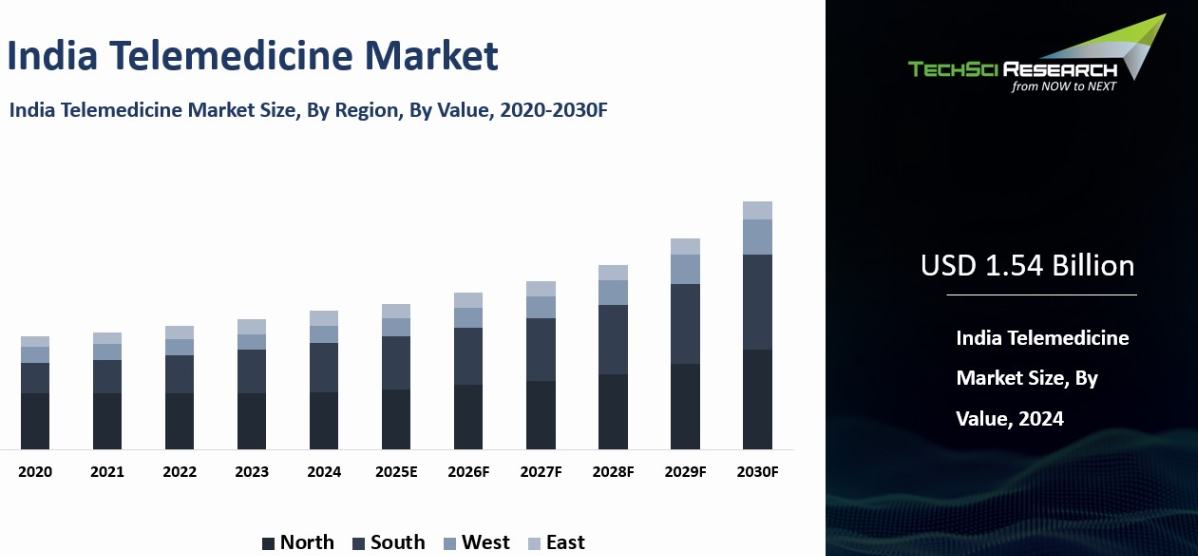
The Telemedicine Market size in India was valued at USD 1.54 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 4.73 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 20.75% during 2025-2030.
Telemedicine, or telehealth, uses digital communication technology to allow medical professionals to provide clinical and non-clinical services remotely. These include consultations, examinations, diagnoses, and treatments delivered through tools such as remote patient monitoring (RPM), mobile health (mHealth) applications, and video conferencing. This approach has reshaped how healthcare is delivered by improving access, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency.
Through telemedicine, healthcare professionals can issue or renew prescriptions, share medical advice, and monitor patients without requiring in-person visits. It supports teleconsultation, telemonitoring, and medical education, making it valuable across different areas of healthcare.
Telemedicine services are delivered through web-based, cloud-based, and on-premises systems. Web-based and cloud platforms provide broad accessibility, suitable for general healthcare use, while on-premises systems are often used in specialized facilities that require greater control and data security. Each mode offers flexibility to meet varying needs of healthcare providers and patients.
By enabling remote access to care, telemedicine helps overcome geographical barriers, especially for people in rural or underserved regions. Its capacity to improve care accessibility, reduce overall healthcare costs, and support better patient outcomes makes it an integral part of modern healthcare delivery.
Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Drivers
Rise In the Demand for Remote Patient Monitoring
The growing burden of chronic diseases and the demand for efficient health management are driving strong growth in India’s Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) market, projected to reach USD 5,670 million by 2035. RPM uses technology to collect patient data outside traditional healthcare settings for conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiac disorders, helping modernize healthcare delivery across the country.
This growth is supported by wider internet access, affordable smart devices, and increasing public acceptance of digital healthcare solutions under the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM). The convenience and accessibility of RPM are expanding care access, especially in remote and rural regions. Collaborations like the one between LifeSigns and RailTel aim to extend AI-driven monitoring services to 1,000 rural and tier-III cities, helping bridge the healthcare gap.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote healthcare, with in-person visits dropping to 32% as online consultations surged. This shift positioned telemedicine and RPM as vital components of healthcare delivery, reducing the risk of infection and maintaining continuity of care. The rise in RPM use is also driving growth in the telemedicine sector.
Government initiatives such as the eSanjeevani platform have strengthened this integration. eSanjeevani has facilitated over 276 million consultations through a network of 127,499 Health & Wellness Centers and 16,211 specialist hubs across the country. The launch of eSanjeevani 2.0 in March 2023, which added point-of-care diagnostic devices, further enhanced the system’s efficiency and accuracy.
The combined use of RPM and telemedicine allows for early detection of health issues, timely medical interventions, and personalized patient care. This integration not only improves health outcomes but also reduces healthcare costs. The rising adoption of RPM is expected to significantly accelerate telemedicine growth in India, supporting broader and more equitable access to quality healthcare.
Rapid Increase in The Aged Population
The rapid growth of India’s elderly population is expected to sharply increase demand for telemedicine services. While India has one of the world’s largest youth populations, it is also undergoing a demographic shift toward aging. The number of people aged 60 and above currently stands at 153 million and is projected to rise to 347 million by 2050. This demographic transition carries major healthcare and social implications that will influence policies, spending, and service delivery across the country.
With age, the prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and arthritis increases, creating the need for frequent medical consultations and monitoring. Regular visits to hospitals or clinics can be difficult for older adults due to mobility issues and the physical strain of travel. Telemedicine addresses these challenges by enabling healthcare professionals to provide consultations, follow-ups, and certain treatments remotely.
This approach improves access and convenience, reducing the need for travel and minimizing waiting times. It also ensures continuous care, which is vital for managing long-term conditions. Telemedicine helps bridge the gap between patients and healthcare facilities, especially in rural and underserved areas where medical infrastructure is limited.
For healthcare providers, telemedicine expands reach and improves the efficiency of care delivery. It allows doctors to monitor patients remotely, adjust treatment plans promptly, and deliver timely interventions. As a result, it enhances patient outcomes and supports the well-being of the elderly population.
The combination of a growing aging population and the benefits of remote healthcare is driving the steady expansion of telemedicine in India. As technology advances and awareness grows, more patients and healthcare professionals are expected to adopt this model, making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and inclusive for the country’s aging population.
Rising Digitization in India
The rapid digitization of India’s economy is reshaping the healthcare sector, driven by a fast-growing internet user base and expanding digital infrastructure. This shift is fueling strong demand for telemedicine services, connecting patients and healthcare providers more effectively. As of January 2025, India had over 806 million internet users, representing a 55.3% penetration rate and ranking as the world’s second-largest online population.
The rise in connectivity is supported by affordable internet and widespread smartphone use. Data costs have dropped from ₹287 per GB to ₹9 per GB, making access to online healthcare affordable for most users. Rural India has become the main growth driver for internet usage, with 488 million users compared to 397 million in urban areas. This is significant, given that about 60% of India’s hospitals are located in cities that house only 32% of the population, while 68% of the population in rural regions faces limited access to quality healthcare.
Telemedicine is emerging as a key solution to bridge this gap. It enables patients in underserved areas to consult doctors, receive diagnoses, and manage treatments without the need to travel long distances. Government programs like the Prime Minister’s Wi-Fi Access Network Interface (PM-WANI) aim to expand public Wi-Fi availability, especially in rural areas, further strengthening the digital foundation needed for telehealth adoption.
The growing comfort with digital interactions is also contributing to the spread of telemedicine. Patients can now consult doctors, receive prescriptions, and order medicines online. This convenience is driving more people to choose remote healthcare options, especially in regions where physical healthcare access is limited.
The Indian government’s National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) reinforces this trend by integrating healthcare services into a unified digital framework. The mission aims to make healthcare delivery more accessible, efficient, and inclusive.
The combination of rising internet penetration, government initiatives, increased digital literacy, and lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic has created strong conditions for the growth of telemedicine in India. With these developments, telemedicine is positioned to close the healthcare access gap and become a central part of India’s future healthcare system.
Key Market Challenges
Lack Of Awareness Particularly in Tier-3 Cities
In India, telemedicine is an immensely beneficial concept that has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery, particularly in remote or underprivileged areas. However, the implementation and acceptance of telemedicine in Tier-3 cities is being significantly impacted by a glaring lack of awareness. Many inhabitants of these regions, which constitute roughly 65% of India's population yet have access to less than 20% of the country's advanced healthcare infrastructure, lack familiarity with the concept, leaving them unable to fully appreciate its benefits.
Despite having technological infrastructure and medical expertise, the potential of telemedicine is not being fully realized due to this knowledge gap. There are also cultural and behavioral factors at play. The traditional method of physical doctor-patient interactions is deeply ingrained in these societies, making it challenging to switch to virtual consultations.
Furthermore, there are concerns about the reliability of remote diagnoses and treatment plans, fueled by a lack of understanding about the technology's capabilities. Language barriers and low levels of digital literacy also contribute to the reluctance to adopt telemedicine, though the use of AI to translate consultations into local languages is emerging as a solution. This unfortunate lack of awareness is expected to hinder efforts to make healthcare more accessible and efficient, even as some digital health platforms report that over 40% of their business now comes from Tier-3 cities.
Unavailability Of Proper Healthcare IT Infrastructure
Despite the myriad potential benefits and recent
advancements in telemedicine, the unavailability of a proper healthcare IT
infrastructure in India is anticipated to hinder its growth. With a vast rural
population, India faces significant challenges in providing equitable
healthcare services.
Telemedicine has been seen as a promising solution to
these challenges, facilitating remote patient monitoring, virtual
consultations, and digital prescriptions. However, the lack of a robust and
comprehensive healthcare IT infrastructure poses a considerable barrier.
Critical concerns include inadequate network connectivity in rural areas,
limited digital literacy among older populations, and a deficiency of
standardized, interoperable systems to facilitate data sharing and
communication between health providers.
Moreover, issues regarding data
security and patient privacy further complicate the implementation of
telemedicine services. As a result, despite the pressing need and potential
benefits, the demand for telemedicine in India is expected to be negatively
impacted by these infrastructural shortcomings. Until these barriers are
addressed, the full potential of telemedicine in transforming healthcare
delivery in India remains untapped.
Key Market Trends
Increasing Prevalence of Various Chronic and Cardiovascular Diseases
The escalating prevalence of chronic and
cardiovascular diseases in India is poised to significantly increase the demand
for telemedicine services. With over 62 million diabetes cases and
approximately 10% of the population being affected by cardiovascular diseases,
India is witnessing a health crisis that mandates immediate attention. The
burden of these diseases not only affects the individuals but also puts a
strain on the healthcare system, leading to increased healthcare costs and
reduced quality of life.
Telemedicine, which involves the remote delivery of
healthcare services, emerges as a suitable solution by bridging the gap between
the patient and the healthcare provider. It negates geographical barriers,
providing immediate access to specialists and facilitating real-time monitoring
of patients' health. This proactive approach allows for early detection and
management of diseases, which is crucial in managing chronic conditions and
preventing the escalation of cardiovascular diseases.
Moreover, telemedicine
offers convenience and flexibility to patients, as they can receive medical
advice and consultations from the comfort of their own homes, reducing the need
for travel and wait times. Considering these factors, it is reasonable to
anticipate a surge in the demand for telemedicine services within the Indian
health landscape.
As the benefits and convenience of telemedicine become more
evident, it is expected that more people will embrace this innovative approach
to healthcare, leading to improved access and better health outcomes for the
population at large. By leveraging technology to overcome the barriers of
distance and time, telemedicine has the potential to revolutionize healthcare
delivery in India and address the growing healthcare needs of the population.
Technological Advancements and The Integration of Chatbots and Robots
Significant technological advancements and the
integration of chatbots and robots on online portals and smartphone
applications have revolutionized the acquisition of personal and health-related
information. These advancements have not only acted as a catalyst for growth
but have also paved the way for enhanced healthcare experiences.
Recognizing the importance of healthcare
information technology (HCIT), the Government of India (GoI) is taking
proactive measures to strengthen the industry. One such measure includes the
provision of telemedicine services, which enable remote monitoring, diagnosis,
and consultation with patients. This innovative approach has proven to be
particularly beneficial during the ongoing coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
epidemic and the subsequent implementation of mandatory lockdowns.
Telemedicine
services have emerged as a preferred choice for outpatient patients seeking
medical care. By leveraging technology, individuals can access healthcare
professionals from the comfort of their own homes, ensuring timely and
efficient medical attention without compromising safety. The GoI's commitment
to expanding telemedicine services demonstrates their dedication to improving
healthcare accessibility and ensuring the well-being of the population. This
not only helps in managing the current healthcare crisis but also sets the
stage for a future where technology plays a vital role in delivering healthcare
services to all.
Segmental Insights
Type Insights
Based on Type, within the telemedicine sector, mHealth, or mobile health, is set to become the dominant segment in India. The widespread adoption of smartphones and growing internet accessibility make mHealth a convenient and cost-effective platform for delivering healthcare services.
mHealth allows patients in even the most remote regions to access essential healthcare, consult doctors, and receive medical guidance without traveling long distances. By overcoming geographical barriers and leveraging digital connectivity, it ensures broader access to quality healthcare. Its user-friendly interfaces and secure communication channels enable seamless interaction between patients and healthcare professionals, providing timely advice and access to important health information.
Integration with technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning further enhances mHealth’s potential. By analyzing patient data, these tools can help providers make accurate diagnoses, predict health trends, and create personalized treatment plans.
Beyond direct patient care, mHealth supports healthcare administration and management. It enables efficient appointment scheduling, remote monitoring of health parameters, and secure sharing of medical records, improving workflow and coordination among healthcare professionals while enhancing overall system efficiency.
Application Insights
Based on application, among the various
applications of telemedicine in India, General Consultations are expected to
dominate the market. This is primarily because a vast majority of healthcare
queries posed by patients can be effectively resolved over teleconsultations.
By leveraging the power of telemedicine, patients can conveniently access
medical advice and guidance from the comfort of their own homes, reducing the
need for physical hospital visits, which is especially crucial during times of
pandemics.
Moreover, general consultations offer a versatile
and accessible form of telemedicine that caters to a broad range of medical
disciplines. Whether it's a common cold, a chronic condition, or a mental
health concern, patients can rely on general consultations to receive
comprehensive healthcare services. This ensures that healthcare services are
readily available to the diverse Indian population, regardless of their
location or specific medical needs.

Download Free Sample Report
Regional Insights
North India is anticipated to experience
significant dominance in the Indian Telemedicine Market in the coming years
North India has been experiencing rapid and progressive technological
advancements, particularly in the healthcare sector. This includes the
implementation of state-of-the-art telemedicine infrastructure and the
integration of cutting-edge technologies to enhance healthcare accessibility
and delivery.
Substantial investments in healthcare infrastructure have
been made in North India, which has resulted in the development of world-class
healthcare facilities and telemedicine centers. These investments have not only
improved the quality of healthcare services but have also created a conducive
environment for telemedicine companies to thrive and innovate. Moreover, North
India boasts a notable concentration of leading telemedicine companies, which
further strengthens its position in the Indian Telemedicine Market. These
companies bring valuable expertise and experience to the region, driving
innovation and pushing the boundaries of telemedicine technology.
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Healthtech firm Pristyn Care announced the launch of three new super-specialty hospitals, signaling a strategic shift from its asset-light model. This move follows its 2022 acquisition of the telemedicine platform Lybrate and is part of a larger plan to own and operate around 50 hospitals by 2028.
- In October 2023, report by insurance tech platform Plum, there has been a notable shift in how individuals access mental health consultations, with distinct preferences emerging between genders. Women have increasingly turned to teleconsultations, accounting for 55% of all mental health consultations conducted online. In contrast, men have demonstrated a clear preference for in-person consultations, comprising 67% of physical appointments for mental health services. This trend underscores evolving consumer behavior in the digital health landscape and highlights differing comfort levels and accessibility preferences between genders in seeking mental health support.
- In July 2023, Lytus Technologies
announced its plan to enter into the Indian market with a focus on
elevating customer experiences through high-value streaming services and
venturing into emerging sectors such as telemedicine and fitness
technology. With India's adoption of 5G services, Lytus Technologies is
strategically positioned to innovate and reshape the landscape of similar
services in the country.
Key Market Players
- Apollo Tele Health Services Pvt. Ltd.
- Practo Technologies Pvt.Ltd.
- TATA 1MG Healthcare Solutions Pvt.Ltd.
- DocOnline Health India Pvt Ltd.
- Lybrate India Pvt.Ltd.
- Netdox Health Pvt. Ltd.
- Allscripts Healthcare Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
- Dhanush Digital Health Pvt. Ltd.
- Novocura Tech Health Services Pvt. Ltd.
- Zoylo DigiHealth Pvt. Ltd.
|
By Component
|
By Deployment Mode
|
By Type
|
By Technology
|
By Delivery Mode
|
By Application
|
By End User
|
By Region
|
- Services & Software
- Hardware
|
|
- Tele-Hospitals
- mHealth
- Tele-Homes
|
- Store & Forward
- Real Time
- Others
|
- Audio-Visual
- Only Audio
- Written
|
- Tele-Psychiatry
- General Consultations
- Tele-Radiology Tele-Pathology
- Others
|
|
|
Report Scope:
In this report, the India Telemedicine Market has
been segmented into the following categories, in addition to the industry
trends which have also been detailed below:
- India Telemedicine Market, By
Component:
o Services & Software
o Hardware
- India Telemedicine Market, By
Deployment Mode:
o Cloud
o On-Premises
- India Telemedicine Market, By
Type:
o Tele-Hospitals
o mHealth
o Tele-Homes
- India Telemedicine Market, By
Technology:
o Store & Forward
o Real Time
o Others
- India Telemedicine Market, By
Delivery Mode:
o Audio-Visual
o Only Audio
o Written
- India Telemedicine Market, By
Application:
o Tele-Psychiatry
o General Consultations
o Tele-Radiology Tele-Pathology
o Others
- India Telemedicine Market, By
End User:
o Patients
o Provider
o Payers
- India Telemedicine Market, By
Region:
o North
o South
o West
o East
Competitive Landscape
Company Profiles: Detailed analysis of the major companies present in the India
Telemedicine Market.
Available Customizations:
India Telemedicine Market report with
the given market data, TechSci Research offers customizations according to a
company's specific needs. The following customization options are available for
the report:
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of
additional market players (up to five).
India Telemedicine Market is an
upcoming report to be released soon. If you wish an early delivery of this
report or want to confirm the date of release, please contact us at [email protected]