|
Forecast
Period
|
2026-2030
|
|
Market
Size (2024)
|
USD
765.60 Million
|
|
Market
Size (2030)
|
USD
1091.62 Million
|
|
CAGR
(2025-2030)
|
6.05%
|
|
Fastest
Growing Segment
|
Generic
Drugs
|
|
Largest
Market
|
Nairobi
|
Market Overview
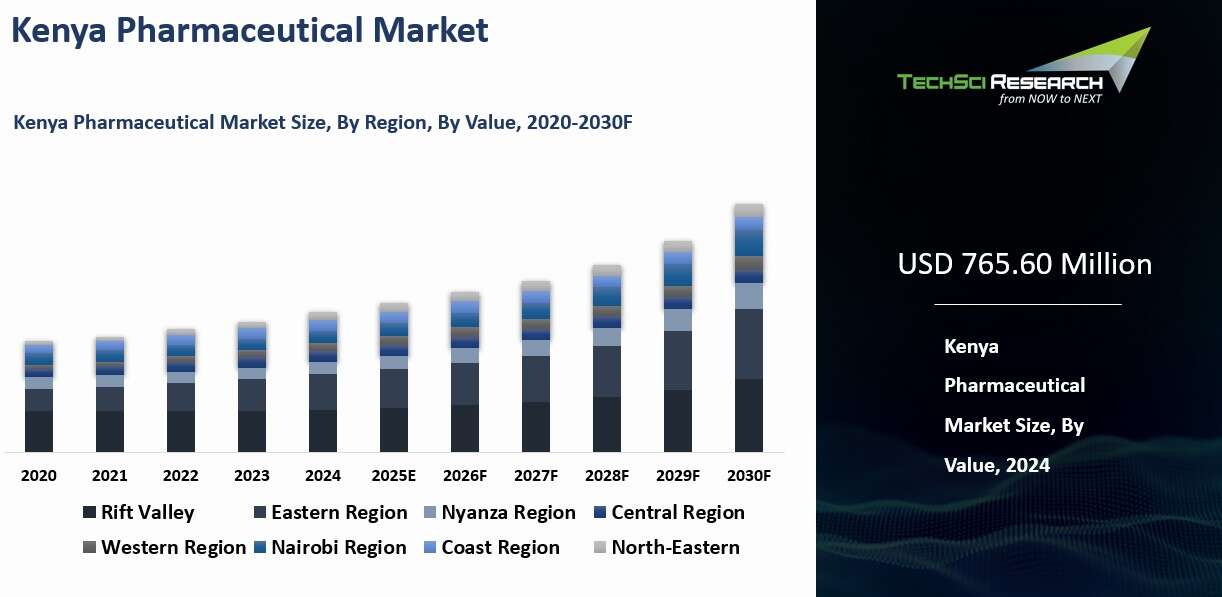
Kenya
Pharmaceutical Market was valued at USD 765.60 Million in 2024 and is
anticipated to project impressive growth in the forecast period with a CAGR of
6.05% through 2030.
The Kenya pharmaceutical market is a dynamic and rapidly
expanding sector, influenced by several key factors, including population
growth, increasing healthcare access, and evolving disease profiles. The market
is currently experiencing robust growth, marked by rising demand for
pharmaceuticals and substantial investments in healthcare infrastructure. It
encompasses a broad range of products, including prescription drugs,
over-the-counter (OTC) medications, and vaccines.
The
surge in Kenya’s population drives up the need for healthcare services and
pharmaceuticals, as a larger population results in a greater number of
individuals requiring medication for diverse health conditions. Urbanization
and enhanced healthcare access further contribute to market expansion,
facilitating increased availability and utilization of pharmaceutical products.
Key
drivers of market growth include changing disease profiles, which necessitate a
range of therapeutic solutions, and technological advancements that enhance
drug development and distribution. The market is characterized by a competitive
landscape that includes both multinational corporations and local
manufacturers. Multinationals offer a wide array of innovative products, while
local companies focus on affordable solutions and addressing regional needs.
Regulatory
support and policies promoting local pharmaceutical production bolster market
development. However, challenges such as distribution inefficiencies, economic
fluctuations, and regulatory compliance issues persist. Despite these
challenges, the market presents significant opportunities for growth and
investment, driven by Kenya’s evolving healthcare sector.
Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Drivers
Growing Population and
Urbanization
The growing population and urbanization in Kenya are driving the expansion of the pharmaceutical market. Kenya’s population growth increases the demand for healthcare services and pharmaceuticals, while urbanization enhances access to these services.
As of 2024, Kenya’s population stands at 56,203,030, a 2% increase from 2023, which had 55,100,586 people, marking a 1.99% rise from 2022. In 2022, the population was 54,027,487, up 1.93% from 2021, and in 2021, it reached 53,005,614, a 1.96% increase from 2020. Population growth leads to higher demand for medications to treat health conditions, prevent diseases, and support overall healthcare needs. A larger population also increases the incidence of acute and chronic conditions, driving demand for both prescription and over-the-counter drugs.
Urbanization further fuels market growth. Kenya’s urban population reached 29.52% in 2024, up 0.5 percentage points (+1.72%) from 2023, the highest share in the observed period. Urban areas concentrate healthcare infrastructure, including hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies, improving access to medications and distribution efficiency. Lifestyle changes associated with urban living, such as altered diets and reduced physical activity, contribute to rising rates of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension, boosting demand for chronic disease treatments.
Urbanization also increases economic activity and individual purchasing power. Higher incomes allow urban residents to spend more on healthcare and pharmaceuticals, both in quantity and quality. The concentration of consumers supports retail and distribution channels, facilitating the establishment of pharmacies, drug stores, and delivery networks. Investments in urban healthcare infrastructure, including modern hospitals and clinics, create demand for advanced pharmaceuticals and medical equipment. Enhanced healthcare services in cities, including specialized treatments, drive consumption of a broader range of medications.
Migration patterns show that 75.25% of household heads reside in rural areas within their districts of origin. Of rural-born individuals, 11.70% have moved to villages in other districts, 13.05% to urban areas, and 5.41% to Greater Nairobi. Governments implement urban health initiatives to address city-specific healthcare needs, including improving access to medicines, subsidizing costs, and enhancing delivery systems. Stronger regulatory frameworks and supportive policies, such as streamlined drug approvals, better safety enforcement, and incentives for pharmaceutical companies, further stimulate market growth in urban areas.
Evolving Disease Profiles
The evolving disease profiles in Kenya are a key driver of pharmaceutical market growth. Shifts in disease prevalence directly influence demand for specific medications and therapies. Kenya is experiencing a notable rise in non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. The prevalence of NCDs varies by region; for instance, diabetes affects an estimated 10.7% of the urban population compared to 2.7% in rural areas.
A study reported that the prevalence of asthma, diabetes, and hypertension ranges from 3.0% in Narok County to 30.2% in Kwale County. This shift from primarily infectious diseases to chronic conditions increases demand for long-term treatment options, including antihypertensives, antidiabetics, and oncology drugs, as well as preventive medications and maintenance therapies. Patients with chronic conditions often require ongoing treatment, creating sustained demand for pharmaceuticals.
Despite the rise in NCDs, infectious diseases such as HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis (TB), and malaria remain significant health challenges. The TB-HIV co-infection rate decreased to 25.2% from 26% in 2019, but the rate among females remains higher at 32% versus 21% among males. HIV positivity stands at 26% among adults and 14% among children. TB continues to pose a major public health concern, with approximately 120,000 annual cases, including 48,000 HIV-positive patients, resulting in around 18,600 deaths and accounting for 6% of all fatalities, ranking as the fourth leading cause of death. Drug-resistant strains, such as multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) and artemisinin-resistant malaria, require new and more effective medications. These challenges drive investment in research and development and stimulate market growth.
Urbanization and lifestyle changes are altering disease patterns. Urban populations are experiencing higher rates of obesity and metabolic disorders, increasing demand for pharmaceuticals addressing obesity, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome. An aging population further contributes to the prevalence of age-related conditions such as osteoporosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and age-related macular degeneration, driving demand for specialized treatments and supportive therapies.
Government and public health initiatives, including malaria prevention campaigns and HIV treatment programs, boost demand for relevant pharmaceuticals. These programs often provide subsidies, awareness campaigns, and expanded healthcare services. Funding from government and international organizations supports research, the development of targeted treatments, and improved medication access, contributing to market growth.
The changing disease landscape encourages pharmaceutical innovation. Advances in drug development, including targeted therapies and personalized medicine, meet patient needs and create new market segments. The rising prevalence of complex conditions also supports the growth of biopharmaceuticals, including biologics and biosimilars, particularly in the treatment of cancer and autoimmune disorders. This expansion provides new therapeutic options and addresses unmet medical needs, further driving the growth of Kenya’s pharmaceutical market.
Expanding Healthcare Access
Expanding healthcare access is a major driver of growth in Kenya’s pharmaceutical market. Improved access increases the population’s ability to obtain medical services and treatments, boosting demand for both prescription and over-the-counter drugs. Programs like Universal Health Coverage (UHC) expand access to medications for various conditions. Between 2013 and 2021, the proportion of for-profit health facilities in Kenya increased from 33% to 43%. Private providers currently account for a large share of medical services, and the Second National Health Strategic Development Plan aims to increase this through public-private partnerships. The National Health Insurance Authority Act 2022, mandating health insurance for all legal residents, is expected to further impact access and demand for pharmaceuticals.
Healthcare expansion drives higher utilization of medical facilities, leading to more diagnoses and prescriptions. Infrastructure improvements, including the construction and upgrading of hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies, enhance availability and distribution of pharmaceuticals. Efficient supply chains, logistics, and storage facilities reduce stockouts, ensuring consistent access to medications. UHC subsidies and expanded insurance coverage through the National Health Insurance Fund (NHIF) improve financial access, enabling more people to afford treatments and increasing pharmaceutical sales.
Preventive care and health education also contribute to market growth. Greater access to vaccinations, screenings, and routine checkups increases demand for medications used in disease prevention and management. Strengthened primary healthcare services expand routine medical attention, supporting consumption of pharmaceuticals for both common ailments and chronic conditions.
Efforts to reach rural and underserved populations further expand the market. Mobile clinics, rural health centers, and telemedicine services provide access to populations with previously limited healthcare. Specialized supply chains ensure essential medications are available in remote areas. This geographic expansion opens new opportunities for pharmaceutical companies, increasing overall market reach and driving growth in Kenya’s pharmaceutical sector.
Key Market Challenges
Regulatory Hurdles
The
process of registering and approving new pharmaceutical products in Kenya is
often lengthy and cumbersome. The Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB), the
regulatory body responsible for ensuring the safety and efficacy of drugs, has
stringent requirements that can delay market entry for new medications. These
delays can discourage pharmaceutical companies from introducing innovative
products, thereby limiting market growth.
Regulatory
enforcement can be inconsistent, leading to challenges in maintaining high
standards across the industry. This inconsistency can result in the circulation
of substandard or counterfeit drugs, undermining public trust in the
pharmaceutical market. Ensuring consistent regulatory practices is essential
for fostering a reliable and trustworthy market environment. Meeting regulatory
requirements involves significant costs, including fees for product
registration, quality control measures, and compliance with Good Manufacturing
Practices (GMP). These costs can be prohibitive for smaller local
manufacturers, restricting their ability to compete with larger multinational
companies and limiting overall market growth.
Inadequate Infrastructure
The
pharmaceutical supply chain in Kenya faces several inefficiencies, including
inadequate storage facilities, poor transportation networks, and logistical
challenges. These inefficiencies can lead to frequent stockouts, spoilage of
temperature-sensitive medications, and delays in getting products to market.
Improving supply chain infrastructure is crucial for ensuring a steady and
reliable supply of pharmaceuticals.
There
is a shortage of healthcare facilities, especially in rural and underserved
areas. This limitation restricts the distribution and accessibility of
pharmaceutical products. Patients in these regions often have to travel long
distances to access medical care and medications, reducing overall market
penetration and growth. The adoption of advanced technologies in the healthcare
and pharmaceutical sectors is still in its nascent stages. Limited
implementation of digital health solutions, electronic health records (EHR),
and automated inventory management systems hampers efficiency and effectiveness
in service delivery. Bridging these technology gaps is essential for
modernizing the market and enhancing growth prospects.
Limited Access to Financing
The
pharmaceutical industry requires substantial capital investment for research
and development, manufacturing, regulatory compliance, and distribution. Access
to financing is a significant challenge for many local pharmaceutical
companies, which often struggle to secure the necessary funds to expand their
operations and invest in innovation.
Financial
institutions in Kenya are often risk-averse when it comes to lending to the
pharmaceutical sector. The perceived risks associated with the industry, such
as regulatory changes and market volatility, make banks and investors hesitant
to provide loans or capital. This risk aversion limits the ability of
pharmaceutical companies to scale their operations and introduce new products. While
there are some government initiatives aimed at supporting the pharmaceutical
sector, the overall level of financial support remains insufficient. More
robust government-backed financing programs, subsidies, and incentives are
needed to encourage investment and growth in the industry. Without adequate
financial support, the market's expansion potential remains constrained.
Key Market Trends
Expansion of Universal
Healthcare Coverage
The
Kenyan government is actively working towards achieving universal healthcare
coverage under its Big Four Agenda, which includes the ambitious goal of
providing affordable and quality healthcare to all citizens. The implementation
of the Universal Health Coverage (UHC) pilot program in select counties has
shown positive results, and plans are underway to roll it out nationwide. This
expansion is expected to significantly increase access to healthcare services
and pharmaceuticals.
Reforms
in the NHIF are aimed at making health insurance more comprehensive and
accessible. By increasing the range of covered services and medications, and
improving the efficiency of claims processing, NHIF is set to drive higher
demand for pharmaceutical products. The fund’s expansion will enable more
Kenyans to afford necessary medications, particularly prescription drugs,
thereby boosting the pharmaceutical market. The government is fostering
partnerships with private sector players to enhance healthcare delivery. These
collaborations are focused on expanding healthcare infrastructure, improving
supply chains, and ensuring the availability of essential medicines. Such
partnerships are crucial for the successful implementation of UHC and will
drive the pharmaceutical market's growth by increasing the availability and
distribution of medicines.
Technological Advancements in
Healthcare
The
adoption of digital health technologies is transforming the healthcare
landscape in Kenya. Telemedicine platforms, electronic health records (EHR),
and mobile health applications are becoming increasingly prevalent. These
technologies improve access to healthcare services, enhance patient management,
and streamline the delivery of medications. For instance, telemedicine enables
remote consultations, reducing the need for physical visits and ensuring timely
access to prescription medications.
Technological
advancements are also revolutionizing the pharmaceutical supply chain. The use
of blockchain technology for tracking and tracing pharmaceutical products
ensures the authenticity and integrity of medicines, combating issues such as
counterfeit drugs. Additionally, the implementation of automated inventory
management systems and smart logistics solutions enhances the efficiency of
pharmaceutical distribution, reducing stockouts and ensuring timely delivery. Advancements
in genomics and personalized medicine are opening new avenues for the
pharmaceutical market. Personalized medicine tailors treatments based on
individual genetic profiles, improving the efficacy and safety of therapies. As
genetic testing becomes more accessible and affordable in Kenya, there will be
a growing demand for specialized pharmaceuticals designed for personalized
treatment regimens.
Increasing Role of Local
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The
Kenyan government is actively promoting local pharmaceutical manufacturing
through various initiatives and incentives. Policies aimed at reducing import
dependency, such as tax incentives and subsidies for local manufacturers, are
encouraging the growth of domestic pharmaceutical production. These measures
not only boost local manufacturing but also enhance the availability of
affordable medications.
Strengthening
the regulatory framework to ensure high standards of quality for locally
manufactured drugs is a key focus. The Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB) is
implementing stringent quality control measures and compliance checks to build
trust in locally produced pharmaceuticals. Enhanced regulatory oversight
ensures that locally manufactured drugs meet international standards, fostering
confidence among healthcare providers and patients.
The
development of local manufacturing capabilities is positioning Kenya as a hub
for pharmaceutical exports within the East African region and beyond. Local
manufacturers are increasingly exploring export opportunities to neighboring
countries, leveraging regional trade agreements and partnerships. This
expansion not only drives the growth of the domestic pharmaceutical market but
also enhances Kenya’s position in the global pharmaceutical supply chain.
Segmental Insights
Drug Type Insights
Based on drug type, the Generic Drugs segment dominated Kenya’s pharmaceutical market in 2024. Generic drugs are significantly cheaper than branded medications, making them accessible to a larger portion of the population. In Kenya, where many have limited financial resources, affordability ensures more individuals can obtain necessary medications. Healthcare providers, including hospitals and clinics, often prefer generics due to their cost-effectiveness, helping manage treatment costs, especially in public healthcare facilities with constrained budgets.
Government policies encourage the use and production of generic drugs. The Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB) facilitates registration and approval, supporting market entry. Local manufacturing initiatives reduce dependency on imports, ensure consistent supply, and strengthen the economy. The National Health Insurance Fund (NHIF) covers generic drugs, promoting their use among patients and healthcare providers, reinforcing market dominance.
Rising chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions increase demand for long-term, cost-effective treatments. Expanding healthcare access in rural and underserved areas further drives the need for affordable medications. Kenya’s local pharmaceutical industry, including companies like Dawa Limited, Universal Corporation Ltd, and Cosmos Limited, produces a wide range of generics that meet stringent quality standards. Trust in locally produced generics has grown, boosting acceptance among healthcare providers and patients.
International health initiatives and partnerships, such as the Global Fund and USAID, support the supply of generic drugs, particularly for HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis. These donor programs prioritize cost-effective generics to bridge demand-supply gaps and ensure essential medications reach those in need. These factors collectively sustain the growth of the generic drugs segment in Kenya.
Product Type Insights
The Prescription Drugs segment in Kenya is projected to grow rapidly during the forecast period. Rising non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer increase demand for long-term medication management, driving prescription drug use. Treatment of these conditions relies on prescribed medications to control symptoms, prevent complications, and improve patient outcomes. Infectious diseases, including HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria, also require prescription-based therapies, such as antiretroviral therapy, multi-drug TB regimens, and specific antimalarials, supporting the prominence of this segment.
The National Health Insurance Fund (NHIF) provides coverage for prescription medications, subsidizing costs and improving accessibility. Kenya’s Essential Medicines List ensures a range of prescription drugs are available in public healthcare facilities, boosting their use. Most medical consultations occur in hospitals and healthcare facilities, where prescriptions are issued by professionals, reinforcing the reliance on prescription drugs. Strict regulatory guidelines for prescription dispensation ensure patient safety and proper medication use, further supporting this segment.
Multinational pharmaceutical companies contribute through research and development, bringing new and effective prescription medications to Kenya. Their established marketing and distribution networks ensure wide availability and influence prescribing practices. Prescription drugs undergo rigorous testing and regulatory approval, building trust among healthcare providers and patients. Healthcare professionals’ endorsement of these medications, based on clinical evidence and regulatory approval, drives higher prescription rates. Collectively, these factors underpin the growth and dominance of prescription drugs in Kenya’s pharmaceutical market.

Download Free Sample Report
Regional Insights
Nairobi
emerged as the dominant in the Kenya Pharmaceutical market in 2024, holding the
largest market share in terms of value. Nairobi is the capital city of Kenya
and serves as the primary economic and commercial center of the country. Its
strategic location makes it a central point for distribution and logistics,
facilitating the efficient movement of pharmaceutical products across the
country and even to neighboring regions. The city’s well-developed
transportation network, including Jomo Kenyatta International Airport, further
enhances its connectivity, making it easier to import and export pharmaceutical
goods.
Nairobi
boasts the most advanced healthcare infrastructure in Kenya. It is home to the
country’s leading hospitals, research institutions, and medical schools. These
facilities provide a robust foundation for the pharmaceutical market,
supporting activities such as clinical trials, research and development, and
high-quality patient care. The presence of top-tier healthcare institutions
attracts both local and international pharmaceutical companies looking to
collaborate on research and bring new products to market. A significant number
of pharmaceutical companies, both multinational and local, have their
headquarters or major operations based in Nairobi. This concentration of
companies creates a competitive environment that drives innovation and growth
in the pharmaceutical sector. Additionally, being in close proximity to each
other allows for better collaboration and partnerships, fostering a thriving
pharmaceutical ecosystem.
The
Kenyan government has implemented several policies and regulations that favor
the growth of the pharmaceutical market, many of which are centered around
Nairobi. The Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB), which regulates the
pharmaceutical industry in Kenya, is headquartered in Nairobi. This proximity
to regulatory authorities facilitates smoother compliance and faster approval
processes for new drugs and treatments. Furthermore, government initiatives
aimed at improving healthcare access and affordability often prioritize Nairobi
as a key implementation region, further boosting the pharmaceutical market in
the area. Nairobi is home to some of Kenya’s top universities and medical
schools, which produce a steady stream of highly skilled professionals in the
pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors. The availability of a well-educated
workforce is crucial for pharmaceutical companies, as it ensures that there is
a pool of qualified individuals to drive research, development, and innovation.
Additionally, continuous professional development and training programs
available in Nairobi help keep the workforce updated with the latest
advancements in the field.
Recent Developments
- In August 2025, Japanese trading firm Marubeni Corporation completed its investment in Phillips Healthcare Corporation, expanding its pharmaceutical operations into African countries, including Kenya and Uganda.
- In July 2025, the Kenyan Ministry of Health announced key reforms to strengthen pharmaceutical regulation, enhance digital health systems, and combat counterfeit medicines. The announcement was made at the 21st Annual Scientific Conference of the Kenya Pharmaceutical Association (KPA).
- In June 2025, Universal Corporation Ltd (UCL), a Kenyan manufacturer, delivered over seven million doses of the antimalarial drug SPAQ under a Global Fund order, setting a standard in local production.
- Between July 15th and 26th, 2024, the Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB) hosted a two-week knowledge-sharing visit from the Southern Region Pharmacovigilance Centre of Malawi, Kamuzu University of Health Sciences. As the Regional Centre of Regulatory Excellence for Pharmacovigilance in Africa, this collaboration facilitated the exchange of best practices in drug monitoring, aiming to strengthen surveillance systems and improve patient safety in both countries.
- Also in July 2024, the PPB adopted advanced Near Infrared (NIR) technology, specifically the Pillscan, to enhance drug quality assurance. Provided by the Mission of Essential Medicines and Supplies, this technology enables on-site screening of medical products at PPB regional offices and key entry points. A six-day training session was conducted for PPB staff, county pharmacists, and KEMSA personnel. Supported by the Global Fund, this initiative improves detection of substandard and falsified medicines, reinforcing market oversight and public health protection.
- In April 2024, Kenya’s drug regulator recalled a batch of Johnson & Johnson children’s cough syrup after Nigeria reported elevated levels of diethylene glycol in the Benylin Paediatric brand. This toxic substance has been linked to multiple child deaths in Gambia, Uzbekistan, and Cameroon since 2022, marking one of the most severe global incidents of oral medication poisoning.
Key Market Players
- F.
Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Novartis AG
- GSK plc
- Pfizer, Inc
- Merck & Co., Inc
- AstraZeneca
- Johnson & Johnson
- Sanofi
- AbbVie, Inc
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
|
By
Drug Type
|
By
Product Type
|
By
Application
|
By
Distribution Channel
|
By
Region
|
- Generic
Drugs
- Branded
Drugs
|
- Prescription
Drugs
- Over-The-Counter
Drugs
|
- Cardiovascular
- Musculoskeletal
- Oncology
- Anti-infective
- Metabolic
Disorder
- Others
|
- Retail
Pharmacy
- Hospital
Pharmacy
- E-Pharmacy
|
- Rift
Valley
- Eastern
Region
- Nyanza
Region
- Central
Region
- Western
Region
- Nairobi
Region
- Coast
Region
- North-Eastern
|
Report Scope:
In this report, the Kenya Pharmaceutical Market has
been segmented into the following categories, in addition to the industry
trends which have also been detailed below:
- Kenya Pharmaceutical Market, By Drug Type:
o Generic Drugs
o Branded Drugs
- Kenya Pharmaceutical Market, By Product Type:
o Prescription Drugs
o Over-The-Counter Drugs
- Kenya Pharmaceutical Market, By Application:
o Cardiovascular
o Musculoskeletal
o Oncology
o Anti-infective
o Metabolic Disorder
o Others
- Kenya Pharmaceutical Market, By Distribution Channel:
o Retail Pharmacy
o Hospital Pharmacy
o E-Pharmacy
- Kenya Pharmaceutical Market, By Region:
o Rift Valley
o Eastern Region
o Nyanza Region
o Central Region
o Western Region
o Nairobi Region
o Coast Region
o North-Eastern
Competitive Landscape
Company Profiles: Detailed analysis of the major companies present in the Kenya
Pharmaceutical Market.
Available Customizations:
Kenya
Pharmaceutical market report with the given market data, TechSci
Research offers customizations according to a company's specific needs. The
following customization options are available for the report:
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of additional
market players (up to five).
Kenya Pharmaceutical Market is an upcoming report
to be released soon. If you wish an early delivery of this report or want to
confirm the date of release, please contact us at [email protected]